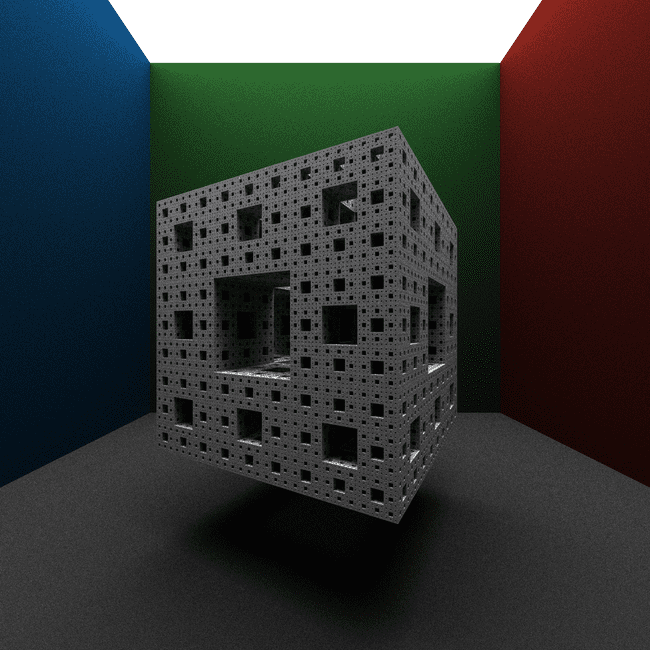
TRM (Tiny Ray Marcher) is a C++ project that implement a very small ray marching algorithm. The project implements the fundamental components of a path tracer, and even provides an easy to use scene definition file.
Efficiency
By changing specific key configuration values in a rendered image, it is possible to significantly alter the quality of the image, in direct relation to the runtime of the program. However some settings will produce a better output image, for less cost to runtime. The main two settings that we consider here, is the spp and the resolution. By doubling the spp it can be considered that we are rendering twice as many images, and combining the images after the fact. While doubling the resolution is equivalent to rendering four times the number of images, and connecting the images as the four quadrants of the output image.
After collecting the data it is clear that doubling the resolution in both axis is indeed about equivalent to four times the samples per pixel. However, increasing the resolution produces a visually shaper images, even with very few samples.
More quantitative data is still being determined.
Configuration
The scene file is based upon JSON file format. The general file is formatted like so:
{
"spp": 128,
"maxiumumDepth": 64,
"resolution": [2000, 2000],
"camera": {
"fov": 1.5707,
"center": [0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
"up": [0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
"pos": [0.0, 0.0, -6.0]
},
"materials": {
...
},
"objects": {
...
}
}General
These are general settings for the render, they control how the renderer will function, and the quality of the produced image. Changing these values will significantly impact the runtime of the renderer. The amount that each value effects the runtime is described in the section on Efficiency.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
spp |
The number of samples per pixel. Higher values will result in better looking images. |
maximumDepth |
The number of bounces that the simulation will simulate before rays begin to terminate. |
resolution |
The width and height of the output image. |
camera |
Information about the camera object in the scene. |
camera.fov |
The field of view for the camera given in radians. |
camera.center |
The point in the scene that the camera will be focused at. |
camera.up |
The direction that will be the up direction relative to the camera. |
camera.pos |
The position of the camera object in the scene. |